[ad_1]
The primary few weeks of a human embryo’s improvement are shrouded in thriller. Researchers can’t observe embryos which are nestled away of their mom’s womb till they’re giant sufficient to be detected by ultrasound, about three weeks after conception. Few human embryos are donated to analysis, and rules in lots of international locations stop these few from being studied past a stage equal to 14 days of pure improvement.
Researchers want inventive methods to check human improvement with out utilizing precise human embryos. One reply lies in stem cells, which, below the best situations, might be coaxed to type embryo-like constructions that may be studied in vitro.
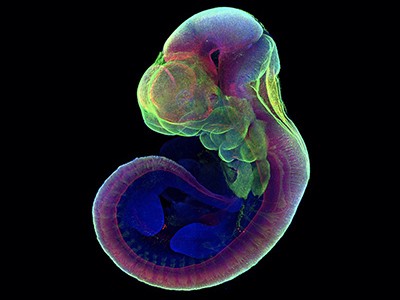
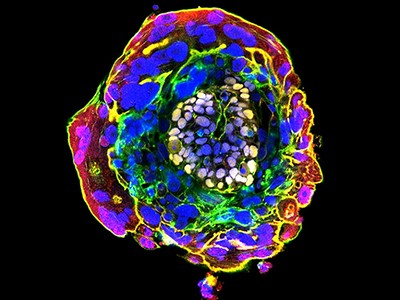
Now three groups writing in Nature1–3, together with others4–6, have used stem cells to generate fashions of the human embryo which are extra superior than these beforehand out there. These new constructions are what are generally known as built-in embryo fashions, as a result of they include tissues which are consultant of elements of the embryo itself in addition to the encircling ‘extraembryonic’ constructions such because the yolk sac that develop with the embryo and help its improvement. These fashions mimic a key week in human improvement, from simply earlier than the embryo implants into the uterus wall at about day 7, till as much as or simply previous the 14-day mark, when the embryo begins making ready to type the primary differentiated layers of tissue. This can be a few days later than has been achieved by different built-in embryo fashions, and a number of the newest fashions include extra tissue varieties than in earlier makes an attempt.
The subsequent frontier for human embryo analysis
These constructions add to a rising toolbox of embryo fashions7,8 that might assist to uncover the occasions that result in early being pregnant loss — a vital space of research, on condition that about 60% of human pregnancies fail within the first 14 days, in keeping with one estimate9. The hope is that they may assist researchers to design higher reproductive applied sciences, discover methods to scale back miscarriages and deal with congenital ailments.
However the present work additionally raises the controversial notion of a doable future during which embryo fashions may very well be grown for longer to supply one thing that might be thought-about ‘human’10,11. Though that is removed from present actuality, many researchers are involved that media hype round such concepts would possibly mislead the general public into pondering that scientists are attempting to develop people from stem cells, and so erode their belief in scientific analysis.
To reduce the danger of future controversy, and keep away from a number of the sensible and moral challenges of producing built-in fashions, we argue that this method needs to be used with warning. We name on researchers to fastidiously outline the scientific questions they want to deal with and to think about essentially the most applicable embryo mannequin for his or her function. In lots of circumstances, less-controversial ‘non-integrated’ human embryo fashions that mimic solely sure elements of improvement can deal with urgent analysis questions equally nicely.
Built-in human embryo fashions
Human embryo fashions are thought-about to be ‘built-in’ if — like these just lately reported — they include embryonic and extraembryonic tissues that collectively give them the potential to supply one thing much like an intact human embryo. Fashions are thought-about ‘non-integrated’ in the event that they lack a number of the tissue varieties wanted for this. Built-in fashions fall into two classes on the idea of the developmental phases they intention to repeat.
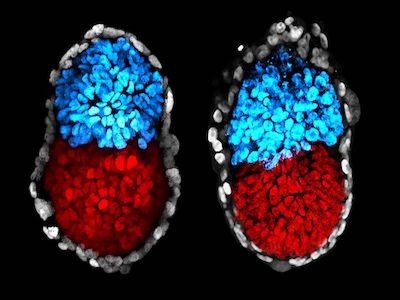
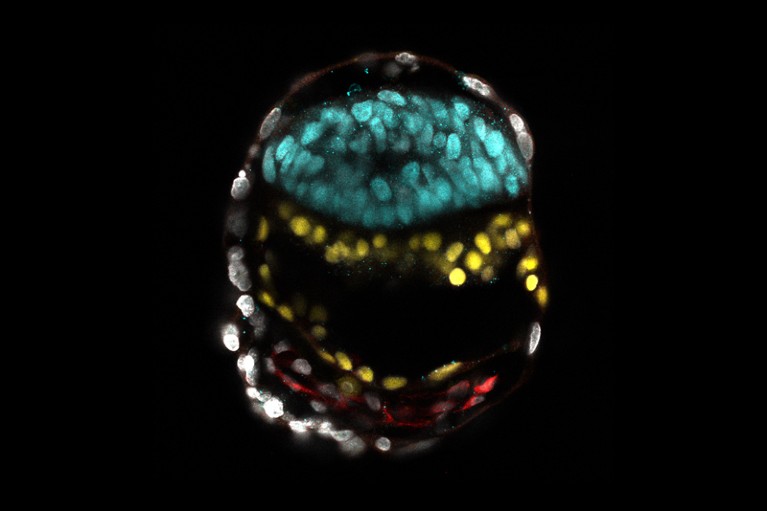
The primary mimics the preliminary few days of human improvement, when the fertilized egg divides a number of occasions to supply a ball of ‘epiblast’ cells, which go on to type the embryo, and a surrounding sphere of extraembryonic cells that go on to generate the placenta. These fashions, known as blastoids, are generated by confining human stem cells in microwells and treating them with chemical substances to set off their progress and differentiation. Blastoids are much like equivalent-stage human embryos of their dimension, form and gene-expression profile. As a result of blastoids might be generated in giant numbers, they can be utilized to display for chemical substances that may enhance in vitro fertilization (IVF) therapies12.

Human embryo fashions grown from stem cells look related in form and construction to pure embryos 14 days after conception.Credit score: B. Oldak et al./Nature
One limitation of human blastoids is that, as with pure human embryos grown in tradition, they at the moment don’t develop nicely past a stage equal to when the pure embryo implants within the uterus wall. But the 2 to a few weeks that comply with implantation are notably essential. Throughout this time, the embryo undergoes a course of known as gastrulation, during which the epiblast cells grow to be organized into layers of embryonic tissues that outline the fundamental physique plan. The primitive coronary heart, early mind and spinal twine, blood and placenta are then fashioned.
The second sort of built-in human embryo mannequin — which incorporates lots of the fashions reported within the newest research1–5 — is designed to imitate the phases of improvement after implantation, when the embryo begins to arrange for gastrulation. By skipping the primary week of human improvement, these fashions bypass the implantation barrier confronted by blastoids and develop to a stage equal to 14 days of pure embryo improvement. Some fashions are designed to imitate all the human embryo1,3 together with all of the cell varieties wanted to type the supporting membranes, that are essential for a profitable being pregnant (the amnion, yolk sac and placenta). Different approaches are much less full, as a result of they exclude the ‘trophoblast’ cells required for placenta formation2,4,5.
These ‘post-implantation’ fashions are the one option to totally visualize the developmental occasions which are normally hidden within the uterus. However there are challenges related to growing and utilizing these approaches.
What’s an embryo? Scientists say definition wants to alter
There isn’t a good commonplace towards which to benchmark post-implantation fashions, as a result of researchers can’t research pure human embryos — and even monkey embryos, that are the closest equal — in any depth after they implant within the womb. This makes it tough to gauge how carefully every mannequin resembles regular human improvement.
Protocols are at the moment inefficient. Researchers at completely different laboratories begin out with completely different sorts of stem cell and so they tradition the cells below completely different situations, making it onerous to match how nicely every mannequin replicates human improvement. Moreover, built-in fashions geared toward mimicking post-implantation improvement typically include disorganized cell varieties and tissue constructions1–5.
One cause that’s generally given for growing built-in post-implantation fashions is to check developmental occasions that happen within the weeks after gastrulation, such because the formation of the guts, the event of the placenta and the era of the ‘neural tube’ tissue that goes on to type the mind and backbone. This could require rising these fashions for per week or two longer in tradition than is at the moment doable. Mouse embryo fashions grown in specialised tradition chambers can develop previous gastrulation and start forming organ rudiments13,14 — classes from these programs may be relevant to human fashions.
Nonetheless, the truth that it’d someday be doable to develop built-in human embryo fashions for prolonged durations of time raises severe moral and regulatory considerations. Ought to these fashions be considered and controlled as if they had been human embryos? And, in that case, ought to the 14-day restriction be utilized?
Take into account alternate options
Clearly, a excessive bar needs to be set for growing stem-cell-based fashions which are meant to copy a full embryo. Researchers ought to ask themselves: ‘Am I making this mannequin for robust scientific causes?’, ‘Is there no different different system?’ and ‘Am I ready to defend my work within the court docket of public opinion?’.
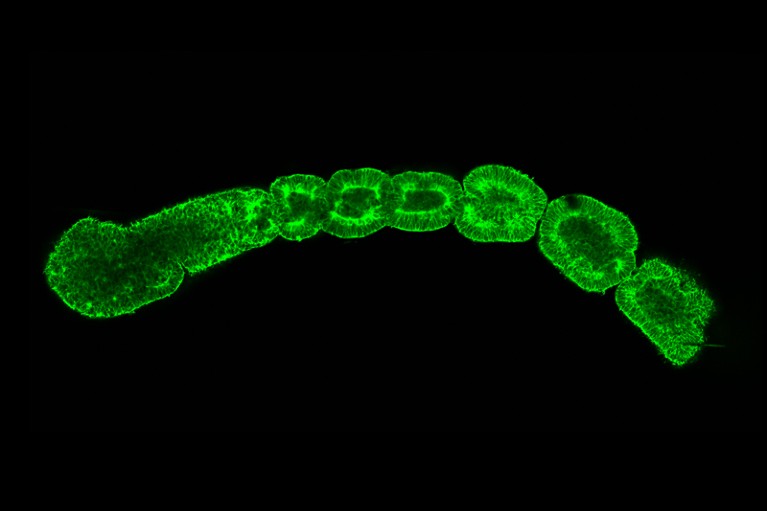
Human stem cells can be utilized to mannequin particular person elements of improvement — as an illustration mimicking blocks of somite tissue from which vertebrae type.Credit score: M. Sanaki-Matsumiya et al./Nature Commun. (CC BY 4.0)
Different stem-cell-based fashions can be found that mimic some elements of human improvement, together with gastrulation and early organ formation7,8. These non-integrated fashions pose fewer moral challenges than do built-in ones. They don’t include all of the cell varieties wanted for a human fetus to develop, however have a number of different helpful properties. As an illustration, they’re simpler to check — they include clearly outlined cell varieties, with the cells organized into common patterns, in contrast to the usually disorganized tissues present in most present built-in fashions. And these different fashions are sometimes constructed utilizing bioengineering instruments resembling custom-made tradition surfaces15 or tiny fluidic chambers by way of which chemical substances might be channelled to regulate stem-cell progress and differentiation16. These instruments permit researchers to tightly regulate the situations that the fashions are grown in, making protocols extra environment friendly, reproducible and scalable.
Non-integrated fashions, by definition, should not good replicas of regular improvement. However right here we define three conditions during which non-integrated fashions might present an excellent different to built-in ones.
Debate ethics of embryo fashions from stem cells
Proponents of constructing built-in human embryo fashions assert that solely full programs can inform us how the entire advanced embryo grows. However many elements of the second week of improvement might be studied with out utilizing built-in fashions. Researchers can effectively develop fashions of the human epiblast utilizing bioengineering instruments15,16. As a result of these non-integrated approaches lack some extraembryonic cell varieties, they may by no means type a fetus with its placenta. But, they’ll nonetheless be used to mannequin the event of the amniotic membrane (which is fashioned from epiblast cells), to analyse how the epiblast develops into completely different tissue layers throughout gastrulation, and to research the early phases of an embryo’s sperm and egg formation, which happens throughout gastrulation.
Non-integrated fashions present a simple option to research the early improvement of the placenta, which is restricted or missing in present built-in post-implantation fashions. Particularly, human trophoblast cells might be guided to type 3D constructions, known as trophoblast organoids, to check placenta improvement17.
The various challenges concerned in rising built-in fashions previous the 14-day mark might be averted just by utilizing current non-integrated fashions that mimic elements of organ improvement. As an illustration, human stem cells might be coaxed to type somites — blocks of tissue from which the vertebrae develop (reviewed in refs 7,8). These fashions can be utilized to discover how the skeleton across the spinal twine kinds and is altered in situations resembling scoliosis. Fashions of neuronal tissue developed from human stem cells are already offering insights into the mechanical forces concerned in bending a sheet of cells right into a closed neural tube, and into the origins of neural-tube defects18. And a few non-integrated fashions can mimic formation of the spinal twine and of the intestine tube, from which the respiratory and digestive programs type19,20.
Appropriately used, stem-cell-based fashions of human embryonic improvement might remodel our understanding of how human life begins. We ask researchers to fastidiously contemplate whether or not there’s a robust scientific rationale for replicating a complete human embryo from stem cells. Pushing forward with out cautious deliberation dangers a public backlash that might stall the progress on this thrilling subject.
[ad_2]