[ad_1]
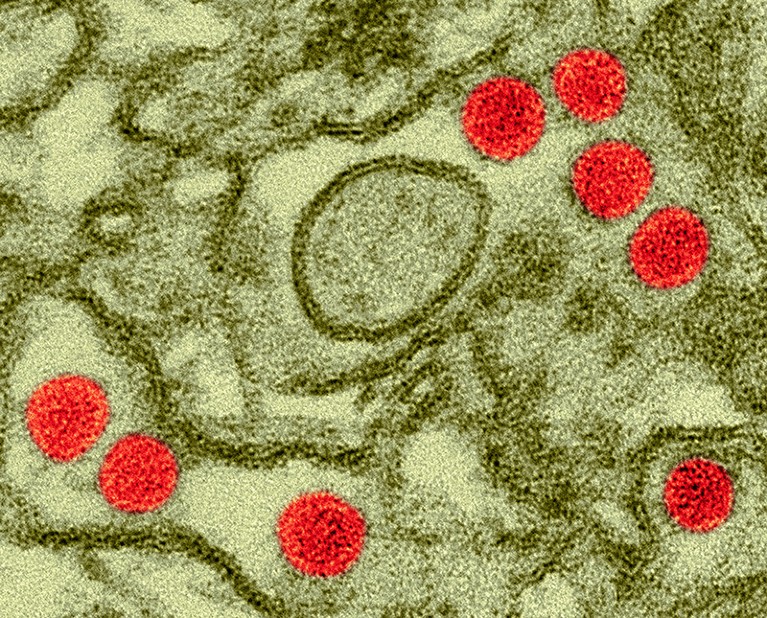
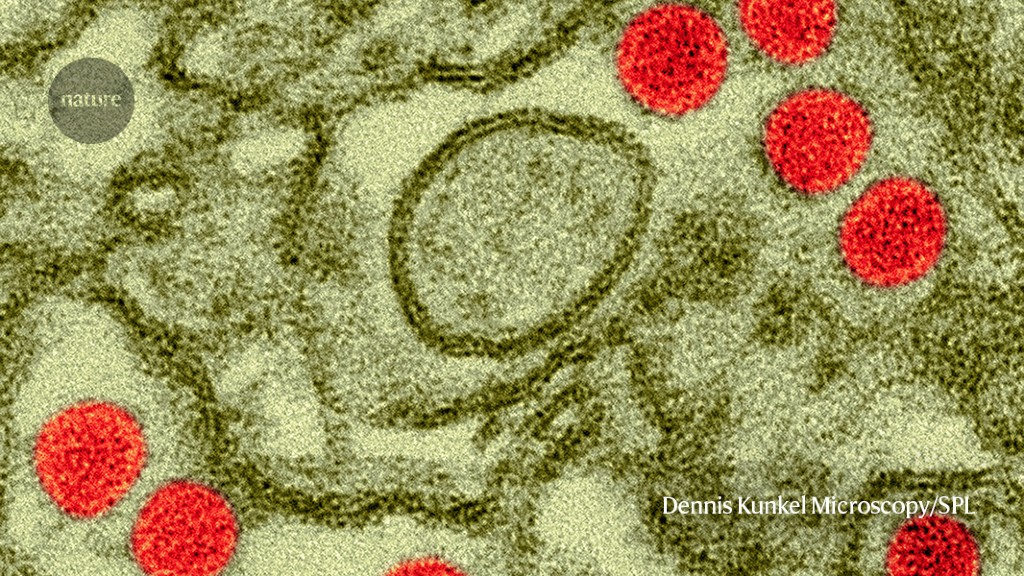
Scientists gave doses of Zika virus (crimson; artificially colored) to wholesome volunteers within the hope {that a} related protocol could possibly be used to trial vaccines.Credit score: Dennis Kunkel Microscopy/Science Photograph Library
For the primary time, scientists have intentionally contaminated folks with Zika virus to be taught whether or not such a technique might assist to check vaccines towards the pathogen.
The virus could cause extreme beginning abnormalities in infants born to folks contaminated throughout being pregnant. It additionally has been related to neurological issues in adults, though these circumstances are uncommon. However contaminated research members had solely delicate signs, and none grew to become pregnant throughout or instantly after the trial. The outcomes increase hopes that ‘human problem’ programmes — through which volunteers are uncovered to a pathogen in a managed setting — might make it possible to check vaccines at a time when Zika incidence is low.
“It is a nice scientific achieve by way of the event of a vaccine,” stated Rafael Franca, an immunologist on the Oswaldo Cruz Basis in Ribeirão Preto, Brazil. The outcomes are scheduled to be offered right now on the annual assembly of the American Society of Tropical Medication and Hygiene in Chicago, Illinois.
Zika’s rise and fall
A surge of neurological congenital issues related to Zika, which is unfold by mosquitoes, led the World Well being Group (WHO) to declare a public-health emergency of worldwide concern in February 2016. Dozens of vaccine candidates had been proposed. For the reason that preliminary outbreaks, nonetheless, the variety of infections has plummeted, halting the progress of scientific trials.
A whole lot of individuals volunteer to be contaminated with coronavirus
That’s why scientists started to debate human problem research. “Our concern was that the epidemic was waning and that conventional [large] scientific trials for efficacy wouldn’t be capable of be accomplished as a result of there wouldn’t be sufficient circumstances of Zika,” says Anna Durbin, an infectious-disease specialist on the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg College of Public Well being in Baltimore, Maryland, and a co-author of the research.
In 2022, after a protracted course of to handle moral considerations across the research, Durbin and her staff recruited 28 wholesome girls, aged 18 to 40, who had been neither pregnant nor lactating. All agreed to be admitted to a analysis facility and stay there till they had been not infectious; they stayed on the unit for 9 to 16 days. They had been examined for being pregnant a number of instances earlier than receiving the virus, to keep away from the danger of congenital issues related to Zika, and had been counselled to make use of contraception for no less than two months after the research.
Hope for smaller trials
The researchers injected 20 members with one among two strains of Zika virus and eight with placebo. The entire members who acquired the virus had been contaminated; of these, 95% developed a rash — a standard symptom of Zika — and 65% had joint ache. Not one of the placebo recipients had these signs.
Durbin says the findings point out that the 2 strains of Zika administered within the trial might be safely and successfully used to contaminate members in a Zika vaccine trial. She estimates that the managed human an infection mannequin could possibly be utilized in a section III scientific trial for vaccine efficacy with as few as 50 to 100 members. “With the problem mannequin, the place you might have 100% of infections, you would get an efficacy consequence with many fewer folks” than in a standard trial, says Durbin.
However Franca expressed concern that bigger problem research might increase the danger of uncommon neurological negative effects, equivalent to Guillain-Barre syndrome, which causes muscular weak point and typically paralysis. And Durbin says that even after a problem research, it will nonetheless be essential to do a scientific trial involving just a few thousand members, to determine a vaccine’s security.
Change of coronary heart
The brand new research represents a turnaround within the excited about problem trials. In early 2017, a report by researchers convened by the Nationwide Institute of Allergy and Infectious Illnesses and the Walter Reed Military Institute of Analysis concluded that the dangers of a human-infection research for Zika, at the moment, surpassed the potential advantages.
How a easy ‘thanks’ might enhance scientific trials
One of many researchers concerned, Ricardo Palacios, a specialist in vaccine improvement at present primarily based in Siena, Italy, says that he and different authors of the report had been involved about sexual transmission of Zika virus from research members to folks outdoors the research. They usually had been unsure whether or not regulatory authorities would think about this sort of research for a vaccine approval.
However “from that point to now, we learnt lots,” says Palacios. “Now we all know that the danger of the virus being transmitted to a different particular person via sexual relationships is restricted and one thing that may be managed,” he says. And regulators have signalled that they could think about knowledge from human problem trials in vaccine improvement, “particularly for these ailments that don’t have sufficient incidence to check within the subject.”
Regardless of the low variety of Zika circumstances, researchers say that it’s necessary to proceed the efforts to develop a vaccine, as a result of the virus would possibly make a comeback. “Infections are a lot decrease than they had been through the epidemic in 2016. Nonetheless, they’re nonetheless occurring,” says Neil French, an infectious-disease specialist on the College of Liverpool, UK, who’s concerned in a Zika vaccine-development mission. “The justification for a vaccine stays robust.”
[ad_2]